本帖最后由 小篱 于 2015-11-5 14:43 编辑 
GameRes游资网授权发布 文 / 易水寒
寻路这块在游戏中一直很重要,花了点时间研究了下这个问题,主要参考的是《Data Structures For Game Programmers》,其他的算法用普通Console演示就行了,寻路算法还是用一个界面比较好,最近在学Cocos2d-x,就用它了。
1.效果图
用到Cocos2d-x中的基本画线段,画矩形就行了,还有简单的sprite拖动。这demo建了一个线条类,继承CCNode,重写draw方法就行了。在draw方法中简单地调用ccDrawColor4F函数来设置颜色,ccDrawLine来画线条,非常容易,cocos2d-x这些函数封装了opengles中的原始函数,使用非常简单。sprite拖动可以参考这篇文章《cocos2d-x Touch 事件应用的一个例子 》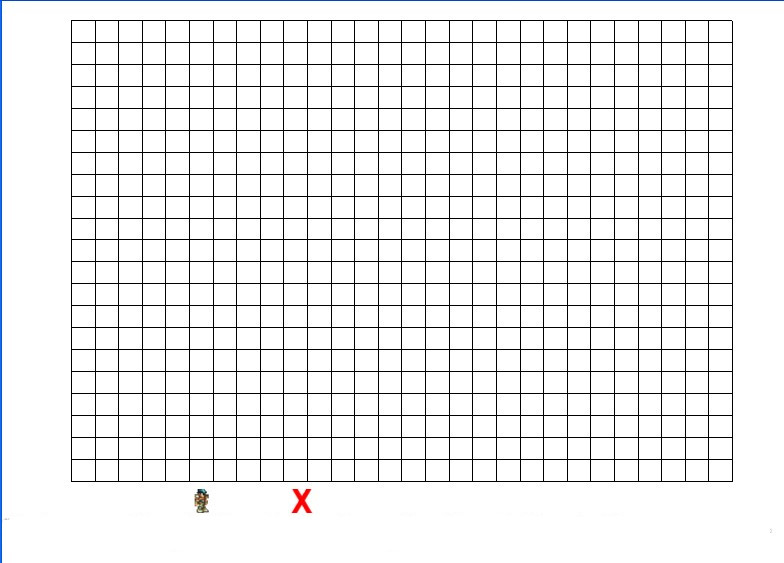
1.小人和红色X都可以用鼠标移动,移到上面的地图上,表示寻路起点和终点。
2.Distance, Simple Heuristic, Complex Heuristic, A Star分别是4种寻路算法,点击程序就会开始演示寻路过程。
3.地图的格子点击会加深颜色,总共4个等级,白,灰,深灰,黑,表示该格子的通过难度,白色是1,灰是2,深灰是3,黑色是不可通过区域。
4.”+++”表示加快演示速度,”—”表示降低演示速度。
2. Breadth – First Search算法
顾名思义,有点像呼吸,一层层地扩展开来,这个时候队列(Queue),stl中的deque就派上用场了。deque不懂可以参考这篇文章《C++ Queue Example Rearranging RailRoad Cars》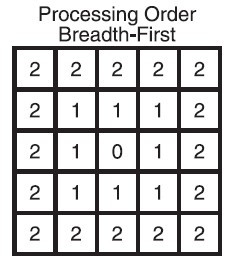
起点在中心,会先访问它的第一个外圈,再是第二个。现在我觉得它更像一颗石头扔在水面上的效果。
下面是伪代码:
- BreadthFirst( Node )
- Queue.Enqueue( Node )Mark( Node )
- While( Queue.IsNotEmpty )
- Process( Queue.Front )
- For Each Child of Queue.Front
- if NotMarked( Child )
- Queue.Enqueue( Child )
- Mark( Child )
- end if
- end For
- Queue.Dequeue()
- End While
- End Function
起点还在中心,这张图显示了每一格到中心的估算距离。如果依靠距离优先的算法,下图是寻路次序:
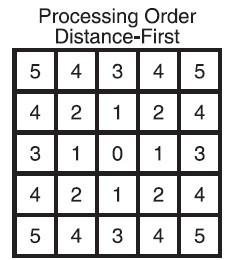
所以我们定义了一个方向数组:
- const int DIRECTION[8][2]={
- {0,1},//north
- {1,0},//east
- {0,-1},//south
- {-1,0},//west
- {1,1},//northeast
- {1,-1},//southeast
- {-1,-1},//southwest
- {-1,1}//northwest
- };
- {-1,1}//northwest
- {-1,-1},//southwest
- {1,-1},//southeast
- {1,1},//northeast
- {-1,0},//west
- {0,-1},//south
- {1,0},//east
- {0,1},//north
这样通过一个for循环,就可以访问它周围一圈的格子了,而且是按照距离优先了,上下左右优先,斜角次些。
因为是地图,我们这里简单定义了一个2维数组,非常简单用一个vector就可以模拟了,假定读者熟悉stl中的vector和C++中的template,不熟悉可以参考这篇文章《STL Vector》和《C++ 基础之 “模版函数”,”类模版”》
- #ifndef ARRAY2D_H
- #define ARRAY2D_H
-
- #include <vector>
-
- using namespace std;
-
- template <class Datatype>
- class Array2D{
- public:
- Array2D(int p_width, int p_height):m_array(p_width * p_height),
- m_width(p_width),m_height(p_height){
- }
- Datatype* Get(int p_x, int p_y)const{
- return m_array[p_y * m_width + p_x];
- }
- void Set(int p_x, int p_y, Datatype* data){
- m_array[p_y * m_width + p_x] = data;
- }
- int Size() const{
- return m_width * m_height;
- }
- int Width() const{
- return m_width;
- }
- int Height()const{
- return m_height;
- }
- private:
- vector<Datatype*> m_array;
- int m_width;
- int m_height;
-
- };
-
- #endif
-
-
- int m_height;
- int m_width;
- vector<Datatype*> m_array;
- private:
- }
- return m_height;
- int Height()const{
- }
- return m_width;
- int Width() const{
- }
- return m_width * m_height;
- int Size() const{
- }
- m_array[p_y * m_width + p_x] = data;
- void Set(int p_x, int p_y, Datatype* data){
- }
- return m_array[p_y * m_width + p_x];
- Datatype* Get(int p_x, int p_y)const{
- }
- m_width(p_width),m_height(p_height){
- Array2D(int p_width, int p_height):m_array(p_width * p_height),
- public:
- class Array2D{
-
-
-
- #define ARRAY2D_H
我们还定义了一个Cell类表示每一个格子:它有很多属性,像位置,最短距离到这个Cell的Cell的位置,是否已经处理过,到起点的距离,是否可以通过,还有就是这个Cell的权重,表示经过难度。我们这里使用了一个从cocos2d-x中拷来的宏,这样get和set方法就不用手写了。
- #ifndef _CELL_H
- #define _CELL_H
-
- #define SYNTHESIZE(varType, varName, funName)\
- protected: varType varName;\
- public: virtual varType get##funName(void) const { return varName; }\
- public: virtual void set##funName(varType var){ varName = var; }
-
- class Cell{
- public:
- Cell():_marked(false),_distance(0),_lastX(-1),_lastY(-1),
- _x(-1),_y(-1),_passable(true),_weight(1),_drawProgress(false){
- }
-
- SYNTHESIZE(int, _x, X); //start at left bottom
- SYNTHESIZE(int, _y, Y); //start at left bottom
- SYNTHESIZE(int, _lastX, LastX); //store the nearest cells location related this cell
- SYNTHESIZE(int, _lastY, LastY); //store the nearest cells location related this cell
- SYNTHESIZE(bool, _marked, Marked); //whether this cell process or not
- SYNTHESIZE(float, _distance, Distance); //distance between this cell and start
- SYNTHESIZE(bool, _passable, Passable); //whether this call can pass
- SYNTHESIZE(int, _drawProgress, DrawProgress); //just for draw the path finding progress
- inline void setWeight(int weight){
- if(weight > 4){
- _weight = 1;
- }else{
- _weight = weight;
- setPassable(weight == 4 ? false : true);
- }
-
- }
- inline int getWeight()const{ return _weight;}
- private:
- int _weight; //default is 1, 4 means this cell is impassable.
- //distance have relationship with weight
- };
-
- #endif
-
- };
- //distance have relationship with weight
- int _weight; //default is 1, 4 means this cell is impassable.
- private:
- inline int getWeight()const{ return _weight;}
-
- }
- setPassable(weight == 4 ? false : true);
- _weight = weight;
- }else{
- _weight = 1;
- if(weight > 4){
- inline void setWeight(int weight){
- SYNTHESIZE(int, _drawProgress, DrawProgress); //just for draw the path finding progress
- SYNTHESIZE(bool, _passable, Passable); //whether this call can pass
- SYNTHESIZE(float, _distance, Distance); //distance between this cell and start
- SYNTHESIZE(bool, _marked, Marked); //whether this cell process or not
- SYNTHESIZE(int, _lastY, LastY); //store the nearest cells location related this cell
- SYNTHESIZE(int, _lastX, LastX); //store the nearest cells location related this cell
- SYNTHESIZE(int, _y, Y); //start at left bottom
-
- }
- _x(-1),_y(-1),_passable(true),_weight(1),_drawProgress(false){
- Cell():_marked(false),_distance(0),_lastX(-1),_lastY(-1),
- public:
-
- public: virtual void set##funName(varType var){ varName = var; }
- public: virtual varType get##funName(void) const { return varName; }\
- protected: varType varName;\
-
- #define _CELL_H
核心算法如下:事先需要了解的知识:因为我们需要按照最短距离优先寻路,所以一个优先队列就需要了,这里简单地使用了heap,对heap不了解的可以看下这篇文章《HeapSort(堆排序 C++) 》,下面还用上了C++中的函数指针,可以参考这篇文章《C++ 函数指针 函数名作为参数 》,为什么要用函数指针呢?看完整个寻路算法系列你就知道了。
语言解释:
先把起点Cell加入到heap中,对这个Cell的周围8个Cell进行处理,主要是更新他们到起点的距离和记录最短距离到这个Cell的Cell的位置。每次找到一个新的Cell,
1.如果还没处理过,标上处理过标志,更新他们到起点的距离和记录最短距离到这个Cell的Cell的位置,再把这个Cell加入到堆中,重新形成一个堆,这样开始很容易得到离起点最近的点。
2.如果处理过,看下新的距离是不是比老的距离短,如果短,更新上面的提到的两点。
不断处理,直到访问了所有的点或者找到终点了。
下面是代码:整个寻路算法的核心代码。
- typedef bool (*compareTwoCells)(Cell *c1, Cell *c2);
- bool compareTwoCellsByDistance(Cell *c1, Cell *c2){
- if(c1->getDistance() <= c2->getDistance()){
- return false;
- }else{
- return true;
- }
- }
- void HelloWorld::startPathFinding(compareTwoCells compareMethod, int startX,int startY,int goalX,int goalY){
- Cell *startCell = _m_Map.Get(startX, startY);
- vector<Cell*> vecCells;
- vecCells.push_back(startCell);
- make_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);
- startCell->setMarked(true);
- Cell *nowProcessCell;
-
- while(vecCells.size() != 0){
- pop_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);
- nowProcessCell = vecCells.back();
- vecCells.pop_back();
-
- if(nowProcessCell->getX() == _goalX nowProcessCell->getY() == _goalY){//the goal is reach
- return;
- }
-
- for(int i = 0; i < 8; ++i){ //check eight direction
-
- int indexX = nowProcessCell->getX() + DIRECTION[i][0];
- int indexY = nowProcessCell->getY() + DIRECTION[i][1];
-
- if(indexX >= 0 indexX < xLineCount indexY >= 0 indexY < yLineCount
- _m_Map.Get(indexX,indexY)->getPassable() == true){//check is a OK cell or not
- Cell *cell = _m_Map.Get(indexX,indexY);
- float beforeDistance = DISTANCE[i] * cell->getWeight() + _m_Map.Get(nowProcessCell->getX(),
- nowProcessCell->getY())->getDistance();//calculate the distance
- if(cell->getMarked() == false){
- cell->setMarked(true);
- cell->setLastX(nowProcessCell->getX());
- cell->setLastY(nowProcessCell->getY());
- cell->setDistance(beforeDistance);
- vecCells.push_back(cell);//only push the unmarked cell into the vector
- push_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);
- }else{// if find a lower distance, update it
- if(beforeDistance < cell->getDistance()){
- cell->setDistance(beforeDistance);
- cell->setLastX(nowProcessCell->getX());
- cell->setLastY(nowProcessCell->getY());
- make_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);//distance change,so make heap again
- }
- }
- }
-
- }
- }
- }
- startPathFinding(compareTwoCellsByDistance,_playerX,_playerY,_goalX,_goalY);//demo
- }
- }
-
- }
- }
- }
- make_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);//distance change,so make heap again
- cell->setLastY(nowProcessCell->getY());
- cell->setLastX(nowProcessCell->getX());
- cell->setDistance(beforeDistance);
- if(beforeDistance < cell->getDistance()){
- }else{// if find a lower distance, update it
- push_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);
- vecCells.push_back(cell);//only push the unmarked cell into the vector
- cell->setDistance(beforeDistance);
- cell->setLastY(nowProcessCell->getY());
- cell->setLastX(nowProcessCell->getX());
- cell->setMarked(true);
- if(cell->getMarked() == false){
- nowProcessCell->getY())->getDistance();//calculate the distance
- float beforeDistance = DISTANCE[i] * cell->getWeight() + _m_Map.Get(nowProcessCell->getX(),
- Cell *cell = _m_Map.Get(indexX,indexY);
- _m_Map.Get(indexX,indexY)->getPassable() == true){//check is a OK cell or not
-
- int indexY = nowProcessCell->getY() + DIRECTION[i][1];
-
-
- }
- return;
-
- vecCells.pop_back();
- nowProcessCell = vecCells.back();
- pop_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);
-
- Cell *nowProcessCell;
- startCell->setMarked(true);
- make_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);
- vecCells.push_back(startCell);
- vector<Cell*> vecCells;
- Cell *startCell = _m_Map.Get(startX, startY);
- void HelloWorld::startPathFinding(compareTwoCells compareMethod, int startX,int startY,int goalX,int goalY){
- }
- }
- return true;
- }else{
- return false;
- if(c1->getDistance() <= c2->getDistance()){
- bool compareTwoCellsByDistance(Cell *c1, Cell *c2){
4.寻路动态图:

我只是简单地在起点和终点间加入了一个不可通过的墙,通过查看蓝色的区域会发现这个算法很慢。目标在右边,这个算法上下左右都找,虽然找到了也太浪费资源了吧?下篇我们来看看其他的寻路算法。
5.项目下载:
(请用7z解压,开发工具vs2010)
http://www.waitingfy.com/?attachment_id=828
http://www.waitingfy.com/?p=820
相关阅读:a寻路算法(for 初学者)

锐亚教育,游戏开发论坛|游戏制作人|游戏策划|游戏开发|独立游戏|游戏产业|游戏研发|游戏运营| unity|unity3d|unity3d官网|unity3d 教程|金融帝国3|8k8k8k|mcafee8.5i|游戏蛮牛|蛮牛 unity|蛮牛
- 还没有人评论,欢迎说说您的想法!





